Data Governance Roles
Data governance defines how an organization will make best use of data whilst also keeping it safe and managed with a reasonable level of cost and resources. Done well, data governance creates a sense of responsibility for data across every person in an organization plus an appreciation of its value to their work.
Of course, not everyone is responsible for everything. An individual will have different skills and interests. Therefore data governance breaks down the work that needs to happen into tasks and groups related tasks into what are called roles.
A role is assigned to a person with a scope. This makes them responsible for performing the tasks for the role, within the assigned scope.
The scope defines the specific data sets and/or processing that this person must perform the tasks for.
For example, the data stewardship role lists all of the tasks related to making a data set fit for purpose, such as correcting errors in it. There may be a data steward assigned to customer records, another for supplier records and another for the financial accounts.
Where data is flowing from system to system, responsibility may be handed off from one data steward to another as the data moves between their scopes of responsibility.
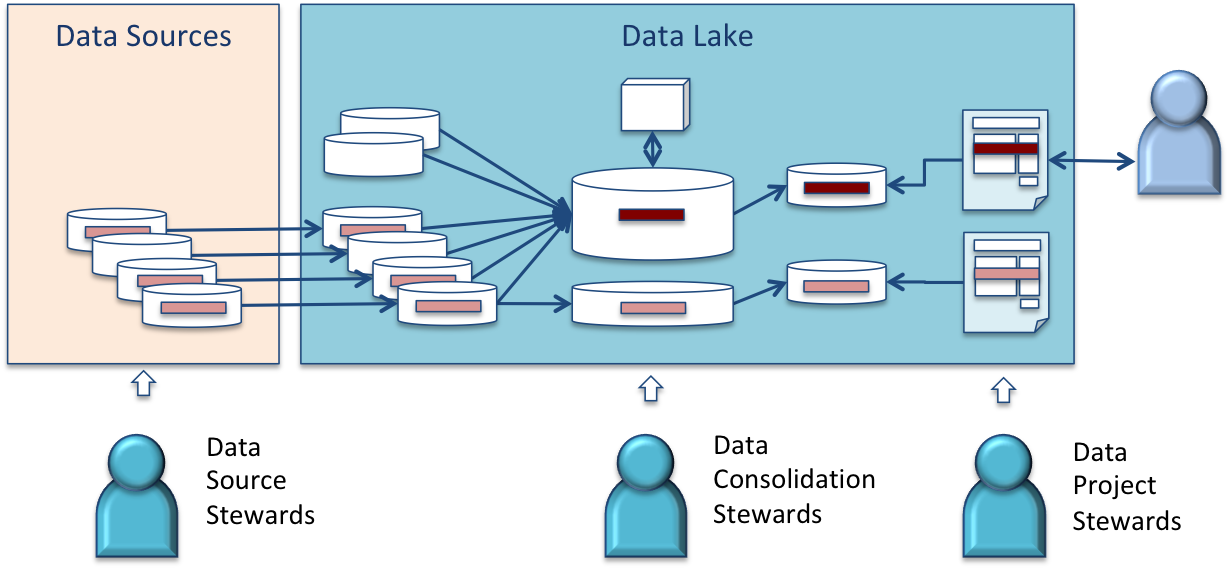
Except in very large enterprises, the data governance roles are typically assigned to individuals in addition to their main role in the organization. Some of these roles are permanently assigned, and other may just be for a project or particular incident.
Roles typically are clustered together defining related types of interactions that need to occur. The roles below are those most important to data governance. In some larger organizations, these roles may be staffed by a dedicated team, or further sub-divided into more specific roles. However, for most organizations, they represent just part of an individual’s responsibility.
Organizational Leadership (general)
Roles that lead in an organization:
External Parties
Roles that interact with the organization:
Governance Leadership roles
Roles that occur when governance programs are in place:
Data Privacy
Roles that lead in data privacy discussions:
Data (and related Asset) Management
Roles involved in the day-to-day use of data (and related) assets:
Digital Services
Roles for building and using digital services:
Return to Guidance on Governance.
License: CC BY 4.0, Copyright Contributors to the ODPi Egeria project.
